
For people with type 2 diabetes, exercise can lower the risk of dying of heart disease. Exercise also can help control weight and boost energy. Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels. Regular exercise helps improve the symptoms of both these conditions.

People who move regularly are at less risk of dementia and problems with learning and thinking. Exercise can improve thinking skills in people with dementia. And it can lower the risk of dying of breast, colorectal and prostate cancers. Exercise can improve the quality of life for people who've had cancer. Stomach and back muscle exercises, also known as core-strengthening exercises, can help ease symptoms by making the muscles around the spine stronger. It can build back strength and make muscles work better. Low-impact aerobic exercise is regular exercise that raises heart rate without putting stress on the body. Often, exercise can help control how often asthma attacks happen and how bad they are.īack pain.

It also can help people with arthritis move better and improve quality of life. Exercise can ease pain, build muscle strength around joints and lessen joint stiffness. Here are ways exercise can help some illnesses. Tai chi, walking backward and practicing standing on one leg are examples of exercises that can improve balance. Balance exercise might prevent falls and lessen injuries from falls. Balance exercises might help lower the risk of falls.Īnother important part of exercise, especially for older adults and people who have trouble moving, is balance. And it can help keep joints stable.įlexibility exercises, such as stretching, can help joints keep moving, so they can work well. It can slow disease-related losses of muscle strength. Strength training can make it easier to do daily activities. Scientific American examines common claims about the benefits of exercise and says that family history and other factors can also play a role in how fitness can have an impact on your overall health.Strength training, such as lifting weights, can improve muscle strength. The Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans are based on years of scientific research, which shows that the longer, harder and more often you exercise-the greater the health benefits. There’s no doubt exercise is good for you, but the degree of benefits varies Does it really matter if you work out three days in a row, rather than spread activity across the week? Yes.

However, “consistent workouts” does not mean that you must work out every day-it’s important to build rest days into your fitness program. Exercising sporadically can decrease motivation, decrease endurance and increase injury. For example, running five miles on one day and then skipping workouts for the next two weeks doesn’t work that well. To realize the benefits of exercise, it’s critical that you participate in physical activity regularly.
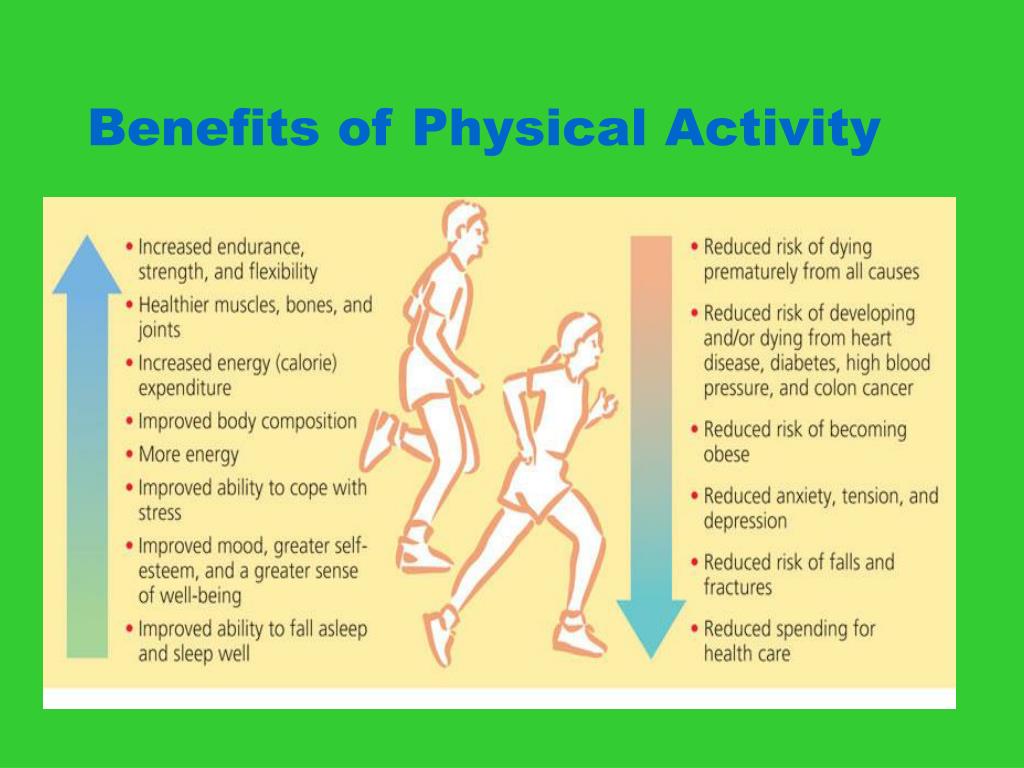
The speed at which intestines empty decreases-exercise can help increase speed.Resting heart rate increases-exercise can help decrease resting heart rate.Harvard Medical School compares the effects of aging with the effects of exercise-and demonstrates that exercise can influence how your quickly your body grows older. Improve your ability to do daily activities and prevent fallsĮxercise can make a positive impact on aging.Reduce risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome and some cancers.The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says ongoing exercise can help: In addition to feeling energized and positive about your progress, regular physical activity is shown to provide a bundle of physical benefits: You might feel challenged to stay motivated-changing up your workouts is a necessary component of a healthy lifestyle. Once you push past the first few weeks of starting a new fitness program, you probably start to notice some changes in how you feel. Long-term benefits of regular exercise Keeping healthy habits over time isn’t easy-but it is worth it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
